Canadian Hydrogen Observatory: Insights to fuel…

Following on from the liberalization of cross-border movements of capital, Hong Kong continues to evolve its regulations with regards to the banking and securities commission: specifically to remain aligned to international standards.
This update from the SIA Partners Financial Services team describes the regulatory environment in Hong Kong and summarizes the forthcoming regulatory changes with analysis of the key changes.
Hong Kong, a city with unique political and economic background in Asia, is raising attention in the international financial markets. Unlike Singapore with a single entity, Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), Hong Kong are maintaining a transparent and robust regulatory structure by products.
The supervision of financial markets in Hong Kong is mainly categorized into 3 sectors: - Banking, Securities & Futures and Insurance.
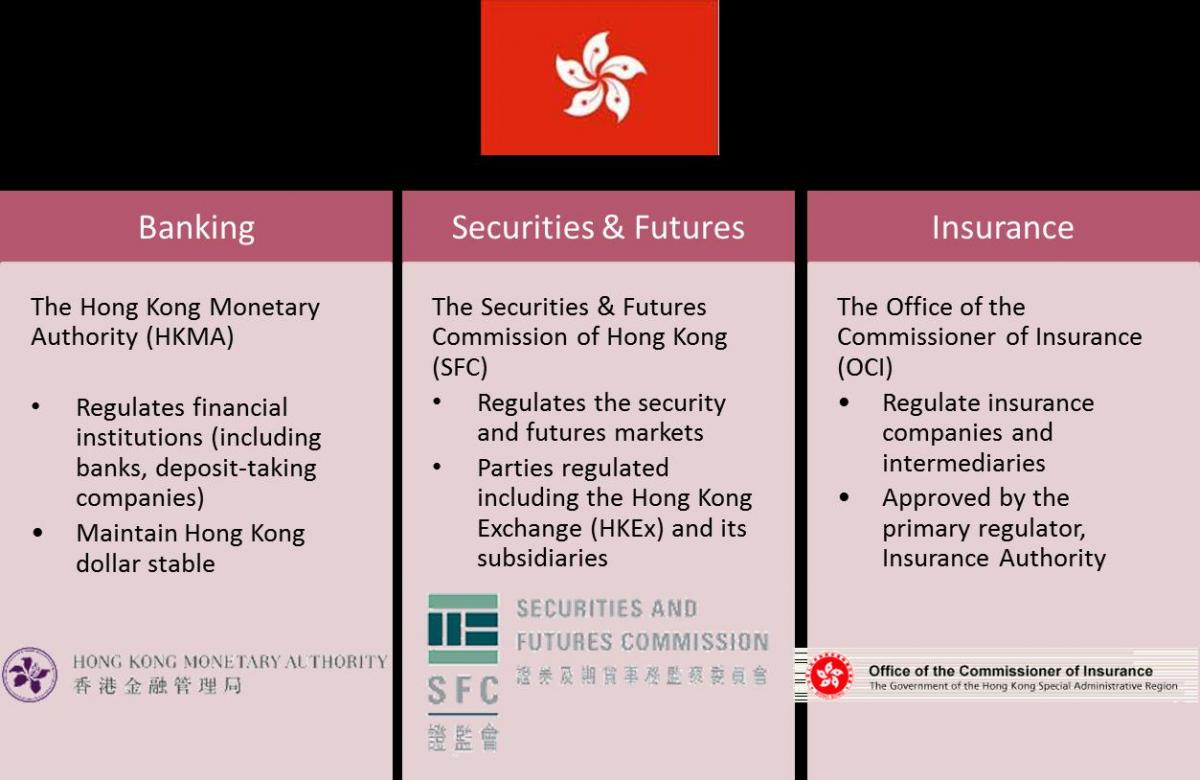
Figure 1. Regulatory framework in Hong Kong financial markets
Apart from these major regulatory parties, there are a couple of other entities that contribute to the stability of financial markets in Hong Kong. For example, the Hong Kong Deposit Protection Board (HKDPB) and Hong Kong Association of Banks (HKAB) for banking activities; the Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing (HKEx) for securities; and Hong Kong Federation of Insurers (HKFI) for Insurance activities.

The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) is the government authority responsible for maintaining monetary and banking stability in Hong Kong. They also promote the safety and integrity of the financial and banking system, maintain and develop Hong Kong's financial infrastructure as well as managing the Exchange Fund.
For monetary stability, HKMA maintains the stability of Hong Kong dollar exchange rate under the framework of the Linked Exchange Rate system (HKD is pegged with USD at 1 USD = 7.8 HKD) through an automatic interest rate adjustment mechanism
For Banking Stability, HKMA regulates and maintain the three-tier banking system: (1) Licensed Banks - Accept deposit with any maturity and size, and pay or collect cheques (2) Restricted License Banks - Accept deposit with any maturity and amounts >= HK $500,000 (3) Deposit Taking Companies - Accept deposit with maturity >= 3 months and amounts >= HK $100, 000. To improve confidence for individual investors on the Hong Kong's banking system, Deposit Protection Scheme Ordinance provides protection up to HK $500, 000 per depositor per bank.
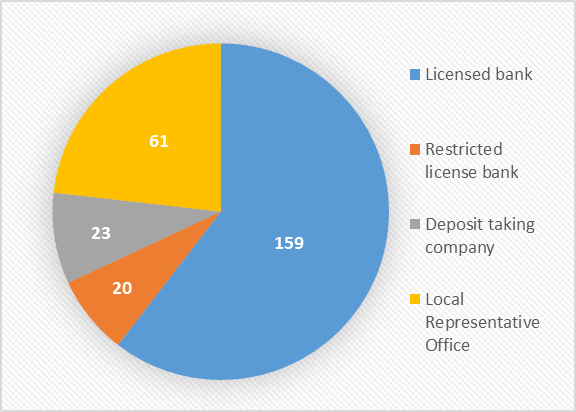
Figure 2. Authorized Institution composition in Hong Kong

The Securities & Futures Commission of Hong Kong (SFC) is an independent statutory body to regulate the securities and futures markets in accordance to the Securities and Futures Ordinance (SFO). SFC is funded by levies on transaction conducted on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEx) and the Hong Kong Futures Exchange (HKFE), and fees charged to license applications. SFC supervises market operators including exchanges, clearing house, issue license and supervises intermediaries and authorizing investment products.

The Office of the Commissioner of Insurance (OCI) is the government authority responsible for supervision of insurers carrying on general insurance business. Their mission is to protect the interests of policyholders and to promote stability of the insurance industry. OCI liaises with industry and professional bodies on regulatory development and publishes statistics on the Hong Kong general insurance market.
Under the regulatory framework in Hong Kong, major regulatory reports that require coverage are:
HKMA sets the standard of financial disclosure in Hong Kong and ensures standards are in line with other leading financial centers. The disclosure standards reflect the financial health of different requirements for Authorized Institutions ("AI"), more detail requirements applies to Locally Incorporated Authorized Institutions than to Overseas Incorporated Authorized Institutions.
SFC enforces market regulation including investigation on market misconduct and defines the Securities and Futures Ordinance. The Ordinance empowers them to collect regulatory reports to monitor the market.
- What happened recently for regulatory changes in Hong Kong?
- What are the coming up regulatory changes to the financial market in Hong Kong?
- How does that impact the reporting requirements for banks?
This article provides an update on regulatory changes for banks and capital market, and insight on the key regulatory changes effective by the end of 2014 (Hong Kong Trade Repository, Banking Returns of International Banking Statistics and Renminbi (RMB) Statistics).
For more details, download the full article.
HKMA, updated as of May 16, 2014